
Inverse relationship between capital price and returns. A discussion with Sal Khan.
- Subject:
- Economics
- Social Science
- Material Type:
- Lesson
- Provider:
- Khan Academy
- Provider Set:
- Khan Academy
- Author:
- Sal Khan
- Date Added:
- 07/27/2021

Inverse relationship between capital price and returns. A discussion with Sal Khan.
What an economist means when they say "investment" is different than what most people mean when they use it in day-to-day conversation. In this video, take a deeper dive into the investment category of real GDP. Created by Sal Khan.

Intuition as to why high real interest rates lead to low investment and why low rates lead to high investment. Created by Sal Khan.

This 9 minute video will explain what a 401(k) is and how a student can use this to build wealth for retirement. This video will enforce standard EPF. 18

This18 minute video will teach students what an Individual Retirement Account (IRA) is and specifically, the Roth IRA. This video will provide examples of how investing through a Roth IRA can build capital for later in life. This video will enforce the standard EPF. 18

This 4 minute video will define term life insurance, who should purchase and why it is cheaper than a whole life insurance policy. This video will aid in the mastery of standard EPF. 14

This 13 minute video will help students understand what an IRA or Individual Retirement Account is and more specifically, what a Traditional IRA is. This video will enforce standard EPF. 18

Is rising inequality necessarily bad? A discussion with Sal Khan.
Analyzing planned expenditures versus actual output using the Keynesian Cross. Created by Sal Khan.
More on shifting aggregate planned expenditures. Connecting to the multiplier. Created by Sal Khan.
Contrasting Keynesian and Classical Thinking. Created by Sal Khan.

How the theory of liquidity preference drives demand for money and the LM (liquidity preference-money supply) curve. Created by Sal Khan.
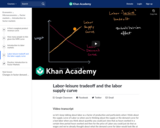
The basis of the labor supply curve is the tradeoff of labor and leisure. When wages increase, the opportunity cost of leisure increases and people supply more labor. Interestingly, this is not always the case! At higher wages, the marginal benefit of higher wages becomes lower and when it drops below the marginal benefit of leisure, people switch to more leisure and less labor. This leads to the rather unusual looking backward bending labor supply curve.
The law of demand states that as the price of a good decreases, the quantity demanded of that good increases. In other words, the law of demand states that the demand curve, as a function of price and quantity, is always downward sloping. In this video, we explore the law of demand and its implications for graphing demand curves. Created by Sal Khan.
In this video we explore the law of supply which states that quantity supplied increases as price increases. We use a supply schedule to describe the quantities a seller is willing to sell at different prices, and then translate the supply schedule into a supply curve that illustrates the law of supply. Created by Sal Khan.
GDP is the most commonly used measure of output, but it leaves some things out. Learn about the limitations of GDP in this video.
Thinking about how real GDP can drive real interest rates. Created by Sal Khan.
How do savers and borrowers find each other? In the market for loanable funds! In this video, learn how the demand of loanable funds and the supply of loanable funds interact to determine real interest rates.
We claim that aggregate supply is not responsive to changes in the price level in the long run, leading to a vertical long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve, but why? In this video we explore why aggregate supply may not be influenced by prices in the long-run. Created by Sal Khan.
In this video we explore the long run average total cost curve and how average costs vary when all inputs can be adjusted.