
Simple model to understand r and g relationship. A discussion with Sal Khan.
- Subject:
- Economics
- Social Science
- Material Type:
- Lesson
- Provider:
- Khan Academy
- Provider Set:
- Khan Academy
- Author:
- Sal Khan
- Date Added:
- 07/27/2021

Simple model to understand r and g relationship. A discussion with Sal Khan.
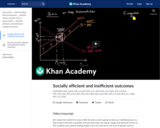
If all costs and benefits are captured by the supply and demand curves, then the market outcome is a quantity where marginal social costs equals marginal social benefit. But what if they don't? In this video, see how markets might produce an inefficient quantity.
Created by Sal Khan.
How a supply shock can cause prices to rise and the economy to stagnate. Created by Sal Khan.
A fourth function of money is that anytime you take on a debt, when the time comes to repay it, you can use money. This is highly related to the idea of "legal tender", which you can also learn about in this video. Created by Grant Sanderson.
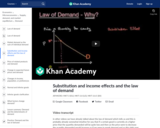
The law of demand states that quantity demanded increases when price decreases, but why? Two reasons why the demand curve slopes downward are the substitution effect and the income effect. The income effect states that when the price of a good decreases, it is as if the buyer of the good's income went up. The substitution effect states that when the price of a good decreases, consumers will substitute away from goods that are relatively more expensive to the cheaper good. Learn about the role of the income effect and the substitution effect on the shape of the demand curve in this video.
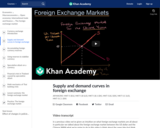
In this video, learn about how the model of the foreign exchange market is used to represent the determination of exchange rates.
When a tax is imposed in a market this is another example of government intervention. In this video, we explore the effect of imposing a tax on the price and quantity in a market. Created by Sal Khan.
An interesting case of taxes and tax incidence is when one of the curves is perfectly elastic. Explore what happens when demand is perfectly elastic in this video. Created by Sal Khan.
The burden of a tax falls most heavily on someone who can't adjust to a price change. That means buyers bear a bigger burden when demand is more inelastic, and sellers bear a bigger burden when supply is more inelastic. Created by Sal Khan.
How to factor in negative externalities through taxation. Created by Sal Khan.
How government can effect aggregate demand through tax policy. Created by Sal Khan.
The spending multiplier and tax multiplier will cause a $1 change in spending or taxes to lead to further changes in AD and aggregate output. The spending multiplier is always 1 greater than the tax multiplier because with taxes some of the initial impact of the tax is saved, which is not true of the spending multiplier.
When a demand curve is linear, calculating consumer surplus becomes relatively simple: calculate the area of a triangle. In this video we walk through calculating consumer surplus. Created by Sal Khan.
The short-run production function describes the relationship between output and inputs when at least one input is fixed, such as out output varies based on the amount of labor used. We can use this production function to find the total product of labor, the marginal product of labor, and the average product of labor.
One of the most practical applications of price elasticity of demand is its relationship to total revenue. A seller who knows the price elasticity of demand for their good can make better decisions about what happens if they raise or lower the price of their good. Explore the relationship between total revenue and elasticity in this video. Created by Sal Khan.
When governments impose restrictions on international trade, this affects the domestic price of the good and reduces total surplus. One such imposition is a tariff (a tax on imported or exported goods and services). See how a tariff impacts price, consumer surplus, producer surplus, tax revenue, and deadweight loss in this video.
The tragedy of the commons occurs when goods are rival but not excludable. In this video, we explore the intuition, and consequences, behind such goods. Created by Sal Khan.

In imperfect competition, firms have some control over the price they charge, so the individual firm's demand curve is not horizontal. Learn how that fact also changes the marginal revenue curve in this video.
Indifference curves for normal goods, substitutes and perfect complements. Created by Sal Khan.