How to account for things when you own the building instead of renting it. Created by Sal Khan.
- Subject:
- Economics
- Social Science
- Material Type:
- Lesson
- Provider:
- Khan Academy
- Provider Set:
- Khan Academy
- Author:
- Sal Khan
- Date Added:
- 07/27/2021

How to account for things when you own the building instead of renting it. Created by Sal Khan.
Where does a buyer's demand curve come from? A rational buyer wants to get as much "bang per buck" from their consumption as possible. In economics, that's called marginal utility per dollar spent. When the price of a good decreases, the "bang per buck" on that good increases, which incentivizes consuming more of it. In this video, we derive the individual's demand curve for a good by tweaking the marginal utility per dollar spent. Created by Sal Khan.
Showing how a change in government spending can lead to a new equilibrium. Created by Sal Khan.
Walk through the logic of determining what kind of good has the most elastic demand in this video.

There are several factors that affect how elastic (or inelastic) the price elasticity of demand is, such as the availability of substitutes, the timeframe, the share of income, whether a good is a luxury vs. a necessity, and how narrowly the market is defined. We explore each of these in this video.

An introduction to the difference between wealth and income. Created by Sal Khan.

In this segment from Curious, learn about creating energy from solar rays to meet the growing energy needs of the world.
Economic growth is an expansion of the capacity to produce goods and services. Economists traditionally believed that expanding the stock of capital leads to economic growth. In this video, we explore the important link between investment and growth using the PPC model. Created by Sal Khan.

This 11 minute video examines the parts of the business cycle and what factors contribute to its fluctuation. This video will aid in mastery of standard EPF. 5(c)

This 5 minute video will examine the how unemployment rate is calculated and the various types of unemployment caused by various economic factors. This video will aid enforcing content of standard 5

Economic models are a way of taking complicated ideas and events and breaking them down into their most important characteristics. We use models in economics so that we can focus our attention on a few things instead of getting bogged down a lot of details. In this video, learn more about the role that models play in economics, and the importance of the assumptions that underlie those models.
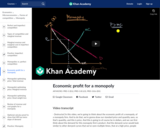
Learn about how to represent a monopoly market graphically in this video. Topics covered include the profit-maximizing quantity, pricing decisions, and deadweight loss associated with monopolies.

An important skill in microeconomics is the ability to find a firm's profit. Learn more about how to use a graph to identify the profit-maximizing quantity for a firm in a perfectly competitive market, and identify the area that represents the firm's profit or loss.
Accounting profit is what many people tend to think of when they think profit, but an economist would say that you leave something very important out when you do so: opportunity costs. In this video, explore the difference between a firm's accounting and economic profit. Created by Sal Khan.

Understanding economics, what some people call "economic literacy," is becoming essential for citizens in our national and increasingly interconnected world economy. Increasingly, productive members of society must be able to identify, analyze, and evaluate the causes and consequences of individual economic decisions and public policy including issues raised by constraints imposed by scarcity, how economies and markets work, and the benefits and costs of economic interaction and interdependence. Such literacy includes analysis, reasoning, problem solving, and decision making that helps people function as consumers, producers, savers, investors, and responsible citizens. - From the Michigan Grade Level Content Expectations
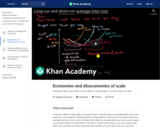
Economies of scale exist when long run average total cost decreases as output increases, diseconomies of scale occur when long run average total cost increases as output increases, and constant returns to scale occur when costs do not change as output increases.
Education as a force of convergence. A discussion with Sal Khan.
Why we calculate percent changes in a strange way when calculating elasticities. Created by Sal Khan.
Thinking about elasticity of supply. Created by Sal Khan.
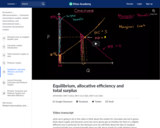
Total surplus is maximized in a market at equilibrium. In this video, we talk about why this is and the math behind this assertion.