Sal gives a conceptual understanding of what center of mass means. Created by Sal Khan.
- Subject:
- Physical Science
- Physics
- Material Type:
- Lesson
- Provider:
- Khan Academy
- Provider Set:
- Khan Academy
- Author:
- Sal Khan
- Date Added:
- 07/15/2021

Sal gives a conceptual understanding of what center of mass means. Created by Sal Khan.

In this interactive activity from NOVA, discover how centripetal force can affect you when riding in a car or flying at high speeds in a fighter jet.

This video segment explains centripetal force and illustrates how roller coasters rely on it to give you a thrilling ride.
Student groups compete to design a process that removes the most iron from fortified cereal. Students experiment with different materials using what they know about iron, magnets and forces to design the best process for removing iron from the cereal samples.
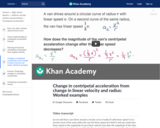
A worked example finding the change in centripetal acceleration from the change in linear speed, and an example finding the change in centripetal acceleration from the change in radius.
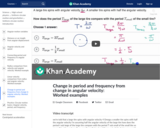
A worked example finding the change in the period from the change in angular velocity, and an example finding the change in frequency from the change in angular velocity.
This lesson begins with an activity in which students induce EMF in a coil of wire using magnetic fields. Then, demonstrations on Eddy currents show how a magnetic field can slow magnets just as Eddy currents are used to slow large trains. There is then a demonstration in which a loop "jumps" because of a changing magnetic field. Finally, formal lecture reviews the cross product with respect to magnetic force and introduces magnetic flux, Faraday's law of Induction, Lenz's Law, Eddy currents, motional EMF and Induced EMF.

This video segment adapted from NASA describes the basic characteristics of our star, the Sun.
Students use balloons to perform several simple experiments to explore static electricity and charge polarization.
Move point charges around on the playing field and then view the electric field, voltages, equipotential lines, and more. It's colorful, it's dynamic, it's free.
Move point charges around on the playing field and then view the electric field, voltages, equipotential lines, and more. It's colorful, it's dynamic, it's free.

In this video segment adapted from NOVA, scientists are on the hunt for tornadoes. Using Doppler radar, they gather data in the hopes of solving the mystery of how tornadoes form.
This lesson introduces the concepts of wavelength and amplitude in transverse waves. In the associated activity, students will use ropes and their bodies to investigate different wavelengths and amplitudes.
Student groups are given captioned photographs of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant facility and surrounding towns taken before and 28 years after the 1986 disaster. Based on the captions and clues in the images, they arrange them in sequential order. While viewing the completed sequence of images, students reflect on what it might have been like to be there, and ask themselves: what were people thinking, doing and saying at each point? This activity assists students in gaining an understanding of how devastating nuclear meltdowns can be, which underscores the importance of responsible engineering. It is recommended that this activity be conducted before the associated lesson, Nuclear Energy through a Virtual Field Trip.
Kinematic equations help solve for an unknown in a problem when an object has either a constant velocity or constant acceleration. This video will help you choose which kinematic equations you should use, given the type of problem you're working through.
Students are introduced to several key concepts of electronic circuits. They learn about some of the physics behind circuits, the key components in a circuit and their pervasiveness in our homes and everyday lives. Students learn about Ohm's Law and how it is used to analyze circuits.
Students use the same method as in the activity from lesson 2 of this unit to explore the magnetism due to electric current instead of a permanent magnet. Students use a compass and circuit to trace the magnetic field lines induced by the electric current moving through the wire. Students develop an understanding of the effect of the electrical current on the compass needle through the induced magnetic field and understand the complexity of a three dimensional field system.
Students learn about gear ratios and power by operating toy mechanical cranes of differing gear ratios. They attempt to pick up objects with various masses to witness how much power must be applied to the system to oppose the force of gravity. They learn about the concept of gear ratio and practice calculating gear ratios on worksheets, discovering that smaller gear ratios are best for picking objects up quickly, and larger gear ratios make it easier to lift heavy objects.

Hydropower generation is introduced to students as a common purpose and benefit of constructing dams. Through an introduction to kinetic and potential energy, students come to understand how a dam creates electricity. They also learn the difference between renewable and non-renewable energy.

Students are challenged to design a method for separating steel from aluminum based on magnetic properties as is frequently done in recycling operations. To complicate the challenge, the magnet used to separate the steel must be able to be switched off to allow for the recollection of the steel. Students must ultimately design, test, and present an effective electromagnet.